This website contains information about
INBRIJA® (levodopa inhalation powder)
M-INB-UK-0047
Date of preparation: December 2025
This website is intended for healthcare professionals from the United Kingdom only. Adverse event reporting information can be found at the bottom of the page.


INBRIJA® 84 mg (n=114) |
Placebo (n=112) |
|
Cough |
15% |
2% |
Upper respiratory tract infection |
6% |
3% |
Nausea |
5% |
3% |
Discolored sputum |
5% |
3% |
2% of 114 patients discontinued INBRIJA® 84 mg due to cough.1
In a one-year safety extension study, patients taking INBRIJA® demonstrated preserved lung function, reflecting long-term respiratory tolerability.2
No additional safety concerns, including dyskinesia, were reported.3
A randomised, controlled, open-label study assessed the effect of INBRIJA® 84 mg (n=271) on pulmonary function vs a control group (n=127) observed on their regular PD medications over 1 year.
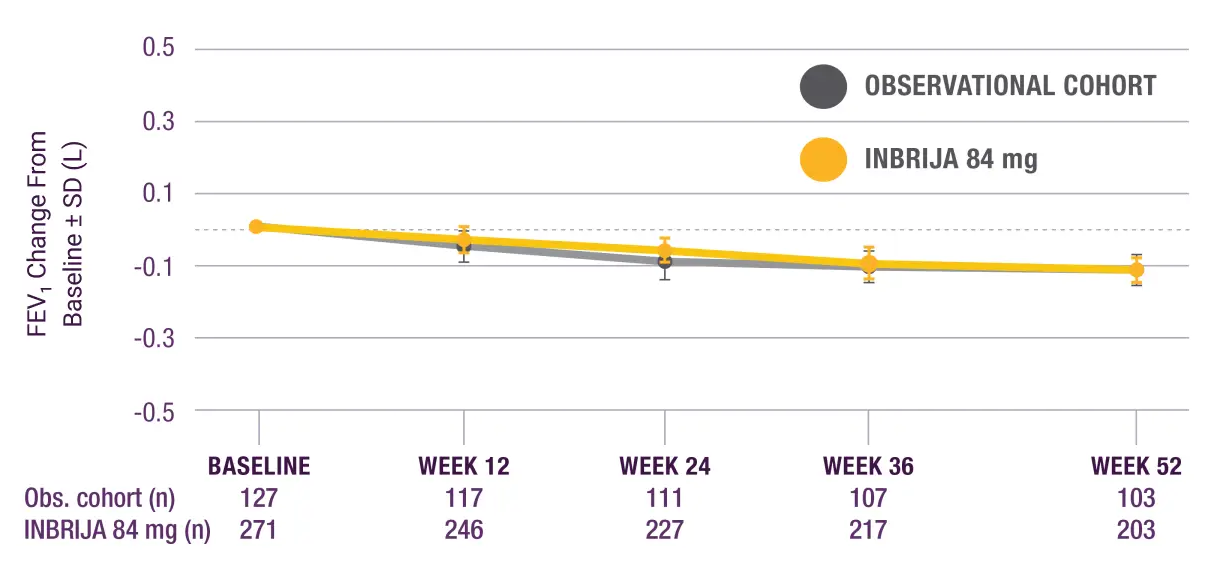
After 1 year, the average reduction in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) from baseline was the same in both the INBRIJA group and observational cohort (-0.1 L).
The most frequent adverse reactions reported in the INBRIJA® clinical studies were cough (15.6%), fall (8.7%), upper respiratory tract infection (5.8%), dyskinesia (5.7%) and sputum discoloured (2.8%). Serious adverse reactions of allergic oedema have been reported with levodopa medicinal products but not in clinical studies with INBRIJA®. Gastrointestinal haemorrhage has been reported with levodopa medicinal products and was observed once in INBRIJA® clinical studies.
| System Organ Class | Very common (≥1/10) | Common (≥1/100 to <1/10) |
|---|---|---|
Nervous System Disorders |
Dyskinesia |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
Cough |
Upper respiratory tract infection, sputum discoloured, nasal discharge discolouration, Throat irritation |
Gastrointestinal disorders |
Nausea, Vomiting |
|
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications |
Fall |
Bronchospasm in patients with lung disease
Because of the risk of bronchospasm use of INBRIJA® in patients with a chronic underlying lung disease is not recommended.
Central Nervous System (CNS) effects and mental disturbances
Cardiovascular ischaemic events: INBRIJA® should be administered in caution with patients with severe cardiovascular disease. Care should be exercised when INBRIJA® is administered to patients with a history of myocardial infarction who have residual atrial, nodal, or ventricular arrhythmias. Cardiac function should be monitored with particular care in such patients during the initiation of treatment with INBRIJA®.
Peptic ulcer disease: Levodopa should be administered cautiously to patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease.
Glaucoma: Levodopa may cause increased intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma. Patients with chronic glaucoma may be treated cautiously with levodopa provided the intraocular pressure is well-controlled and the patient is monitored carefully for changes in intraocular pressure during therapy.
Melanoma: Periodic skin examinations are recommended to monitor for melanoma in patients receiving INBRIJA®.
Orthostatic hypotension: Levodopa can cause orthostatic hypotension. INBRIJA® should be used with caution in case of concomitant use of medicinal products that may cause orthostatic hypotension.
Intercurrent respiratory infection: There is limited data available on the use of INBRIJA® during a respiratory infection. Based on individual assessments of the severity of the intercurrent respiratory infection INBRIJA® may be continued or discontinued until the respiratory symptoms resolve.
Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for full information regarding the above warnings and precautions.
Interaction with other medicinal products:
Selective Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) inhibitors: The use of selective MAO-B inhibitors (e.g. rasagiline, selegiline, and safinamide) with levodopa may be associated with orthostatic hypotension. Patients who are taking these medicinal products should be monitored closely.
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists and isoniazid: Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists (e.g. phenothiazines, butyrophenones, risperidone, metoclopramide) and isoniazid may reduce the effectiveness of levodopa. Patients who are taking these medicinal products should be monitored for worsening Parkinson’s symptoms.
Antihypertensives: Symptomatic postural hypotension has occurred when combinations of levodopa and a dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor are added to the treatment of patients already receiving certain antihypertensives. Dose adjustment of the antihypertensive medicinal products may be required during concomitant use of INBRIJA®.
Anticholinergics: Anticholinergic medicinal products can work synergistically with levodopa, in order to improve tremor. Concurrent use can, however, cause a worsening of involuntary motor disorders. Anticholinergic medicinal products may impair the effect of oral levodopa medicinal products, due to a delayed absorption. A dose adjustment of levodopa may be required.
COMT inhibitors: The addition of entacapone to a levodopa/dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor has been demonstrated to increase the levodopa bioavailability by 30%. A dose adjustment of levodopa may be required with concomitant use of COMT inhibitors.
Tricyclic antidepressants: There have been rare reports of adverse reactions, including hypertension and dyskinesia, resulting from the concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants and a levodopa/dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor.
Amantadine: Concurrent administration of levodopa and amantadine may increase confusion, hallucinations, nightmares, gastro-intestinal disturbances, or other atropine-like side effects. Psychotic reactions have been observed in patients receiving amantadine and levodopa.
Local or systemic pulmonary medicinal products: Interactions of INBRIJA® with local or systemic pulmonary medicinal products were not investigated because Inbrija is not recommended in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other chronic underlying lung disease.
Levodopa may have a major influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Certain side effects such as sleepiness and dizziness, that have been reported with other forms of levodopa medicinal products, may affect some patients’ ability to drive or use machines.
Patients being treated with levodopa medicinal products and presenting with somnolence and/or sudden sleep episodes must be informed to refrain from driving or engaging in activities where impaired alertness may put themselves or others at risk of serious injury or death (e.g. use machines), until such recurrent episodes and somnolence have resolved.
M-INB-UK-0047
Date of preparation: December 2025